Clinical Features and Treatment of Bacterial Infection:
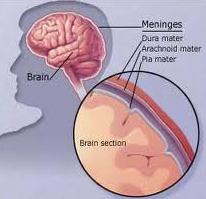 In most cases the infection causing meningitis arises in the nasopharynx intravascular invasion (bacteraemia) and penetration of the blood brain barrier follow mucosal involvement with entry into the CSF. Bacteria may invade the subarachnoid space directly by spread from contiguous structures, e.g. sinuses and fractures. Specific characteristics of the capsule determine whether meninges are breached. Humoral defences against bacteria are absent in the CSF offering little resistance to infection.
In most cases the infection causing meningitis arises in the nasopharynx intravascular invasion (bacteraemia) and penetration of the blood brain barrier follow mucosal involvement with entry into the CSF. Bacteria may invade the subarachnoid space directly by spread from contiguous structures, e.g. sinuses and fractures. Specific characteristics of the capsule determine whether meninges are breached. Humoral defences against bacteria are absent in the CSF offering little resistance to infection.
Clinical Features
The classical clinical traid is
Prodromal Features
A respiratory infection otitis media or pneumonia associated with muscle pain.
Meningitic Symptoms
- Severe frontal/occipital headache
- Stiff neck
- Photophobia
Investigations
- If patient has altered consciousness, focal signs, papilloedema, and a recent seizure or is immunocompromised a CT brain should be done before LP. However, do not delay treatment -take blood cultures and commence antibiotics prior to scanning.
- If above signs are absent or CT scan excludes a mass lesion confirm diagnosis with a lumbar puncture and identify the organism.
Treatment
- Once meningitis is suspected, treatment must commence immediately, often before identification of the causative organism.
- Antibiotics must penetrate CSF, be in appropriate bactericidal dosage and be sensitive to causal organism once identified.
Braner Pain Clinics specialize in chronic pain management, neurology, neurological testing and disability. Our clinics are conveniently located in Northern Virginia minutes away from Interstate 495 (Beltway). Call now for best treatment: (703) 573-1282