Clinical Features of Anterior Cerebral Artery:
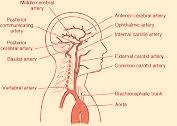 The anterior cerebral artery is a branch of the internal carotid and runs above the optic nerve to follow the curve of the corpus callosum. Soon after its origin the vessel is joined by the anterior communicating artery. Deep branches pass to the anterior part of the internal capsule and basal nuclei. Cortical branches supply the medial surface of the hemisphere:
The anterior cerebral artery is a branch of the internal carotid and runs above the optic nerve to follow the curve of the corpus callosum. Soon after its origin the vessel is joined by the anterior communicating artery. Deep branches pass to the anterior part of the internal capsule and basal nuclei. Cortical branches supply the medial surface of the hemisphere:
Clinical Features
The anterior cerebral artery may be occluded by embolus or thrombus. The clinical picture depends on the site of occlusion (especially in relation to the anterior communicating artery) and anatomical variation, e.g. both anterior cerebral arteries may arise from one side by enlargement of the anterior communicating artery.
Occlusion proximal to the anterior communicating artery is normally well tolerated because of the cross flow.
- Distal occlusion results in weakness and cortical sensory loss in the contralateral lower limb with associated incontinence. Occasionally a contralateral grasp reflex is present.
- Proximal occlusion when both anterior cerebral vessels arise from the same side results in ‘cerebral’ paraplegia with lower limb weakness, sensory loss, incontinence and presence of grasp, snout and palmomental reflexes.
Bilateral frontal lobe infarction may result in akinetic mutism or deterioration in conscious level.
Braner Pain Clinics has a talented and friendly staff. We will do everything in our power to make sure your visit is a satisfying experience. If there is anything else you may need from us, just ask! We are here to serve you. Contact Us at: (877) 573-1282 or Visit Our Website: http://www.branerpainclinic.com